Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or Moab) are identical immunoglobulins, generated from a single B-cell clone. These antibodies recognize unique epitopes, or binding sites, on a single antigen. Derivation from single B-cell clones and subsequent targeting of a single epitope is what differentiates monoclonal antibodies from polyclonal antibodies.
With almost any substance, it is possible to produce a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to that substance; it can then be used to detect or purify that substance. It has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine. There are many companies available that provide high-quality rabbit monoclonal antibodies production services.
How to make monoclonal antibodies
As the generation of polyclonal antibodies, the generation of monoclonal antibodies begins by generating a strong immune response. However, instead of collecting serum from the host to reconstitute the polyclonal antibody population, monoclonal antibody production requires antibody-producing collecting cells, the lymphocytes.
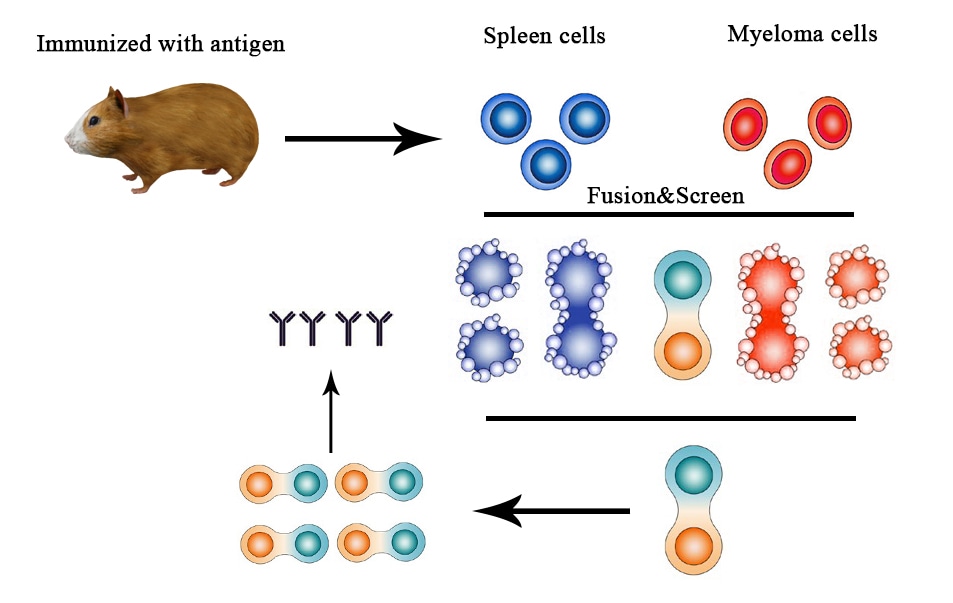
Image Source: Google
Once collected, lymphocytes were immortalized, cloned at limited dilution, examined for proper expression, expanded, and preserved as described below.
• Monoclonal antibody production continues with lymphocyte accumulation
• Production of monoclonal antibodies
• Lymphocyte collection
The production of monoclonal antibodies requires a collection of antibody-producing cells located in the spleen or lymph nodes.
Fusion to produce hybridoma cells
Because spleen cells have a limited survival time in culture, they must fuse with myeloma, a B cancer cell, to create a perennial hybrid that can undergo multiple passages in vitro. This is achieved by polyethylene glycol (PEG) or electrical impulses that disrupt the cell membrane and allow two adjacent cells to fuse.
Options for fused hybrids
B cell fusion and myeloma are not 100% effective. Therefore, selection for myeloma-lymphocyte hybrids is necessary. Hypoxanthine-aminopterin-thymidine (HAT) medium inhibits DNA synthesis by aminopterin.